Acne: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Acne is a common dermatological condition that affects millions of people worldwide, especially teenagers and young adults. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 85% of people aged 12-24 experience acne at some point in their lives. This condition can range from mild to severe, impacting not only physical health but also self-esteem and quality of life for those affected.
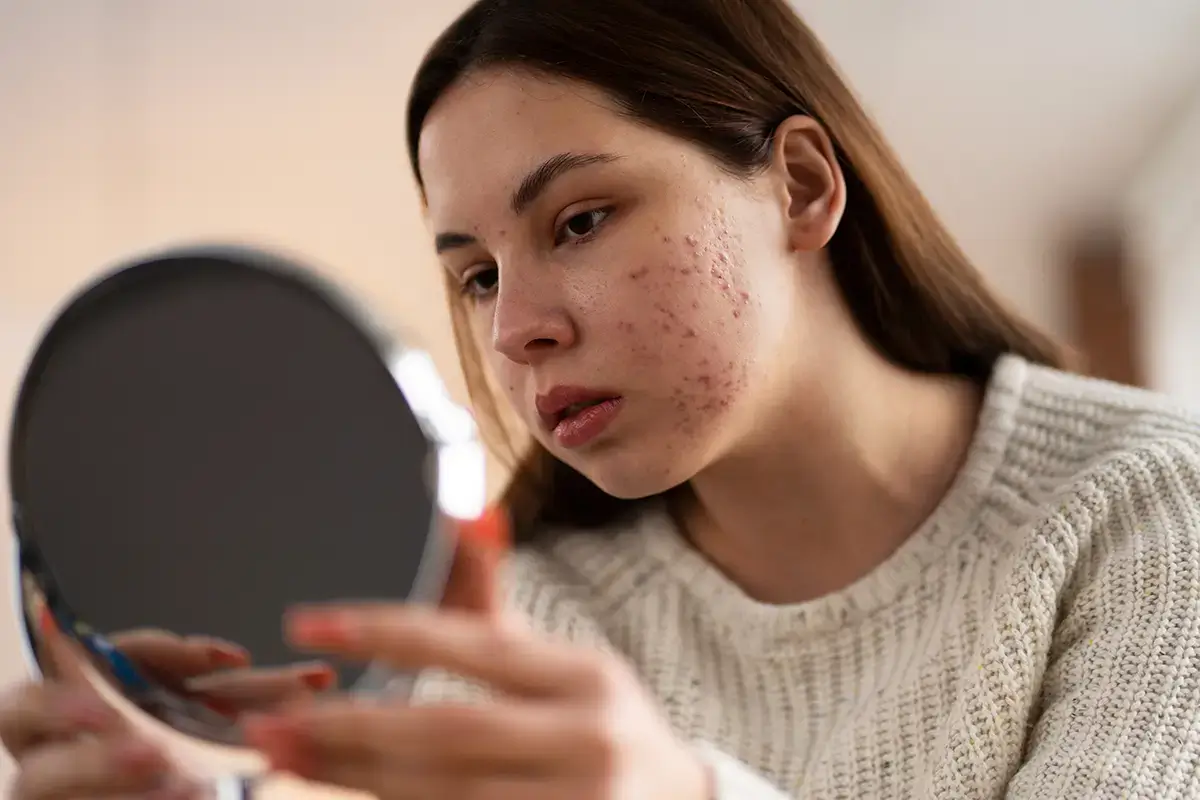
Acne is characterized by the appearance of pimples, blackheads, and, in severe cases, nodules and cysts. The Brazilian Society of Dermatology reports that acne is caused by a combination of factors, including increased sebum production, follicular plugging, and bacterial growth, often associated with hormonal changes during puberty. Understanding the underlying causes and adopting effective treatment and prevention measures are essential to managing this common skin condition.
Symptoms and Types of Acne:
There are different types of acne, ranging from comedones (blackheads) to more severe inflammatory lesions such as papules and pustules. Symptoms may include oily skin, enlarged pores, inflammation, and discomfort in more severe cases. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing scarring.
Risk Factors and Causes:
In addition to hormonal changes during adolescence, other factors may contribute to the development of acne, such as genetic predisposition, stress, a diet rich in processed foods, and improper skin care products. Understanding these risk factors helps personalize treatment and adopt appropriate preventive measures.
Available Treatments:
Treatment for acne may involve a combination of topical care, oral medications, and dermatological procedures. Common options include the use of benzoyl peroxide, topical acids (such as salicylic acid and glycolic acid), oral antibiotics, and, in severe cases, oral isotretinoin. Procedures such as chemical peels, light therapy, and lesion drainage may also be recommended by dermatologists, depending on the severity and type of acne presented.
Prevention and Daily Care:
To prevent acne, it is essential to adopt a daily skin care routine, including gentle cleansing twice a day, use of non-comedogenic products, adequate hydration, and sun protection. Additionally, avoiding excessive makeup use, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing stress are important preventive measures.
Psychological Impact and Quality of Life:
Acne not only affects the physical health of the skin but can also have a significant impact on the mental and emotional health of affected individuals. Issues such as low self-esteem, social anxiety, and depression may arise due to changes in skin appearance. Therefore, psychological support and education about acne are essential for the overall well-being of patients.
Conclusion:
While acne is a common and sometimes frustrating condition, there are many effective treatment and prevention options available. Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With proper care and patience, acne can be managed, significantly improving quality of life.
Sources Consulted:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Ministry of Health
- Brazilian Society of Dermatology