Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Current Treatments
Diabetes, a chronic disease affecting millions worldwide, poses a growing challenge to global public health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Ministry of Health, diabetes is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin production by the pancreas or the body’s ineffective use of insulin. This metabolic disorder can lead to serious complications if not properly managed, significantly impacting the quality of life of those affected and escalating healthcare costs globally.
Recent data indicates that approximately 422 million adults were living with diabetes in 2021, marking a concerning increase compared to previous decades. It is estimated that by 2030, this number could rise to over 580 million, reflecting the alarming trend of global diabetes prevalence growth. Much of this increase is driven by factors such as population aging, lifestyle changes, unhealthy diets, and lack of physical activity.
Types of Diabetes:
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults and occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin due to the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, more common, occurs when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces or when insulin production is insufficient for the body’s needs.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
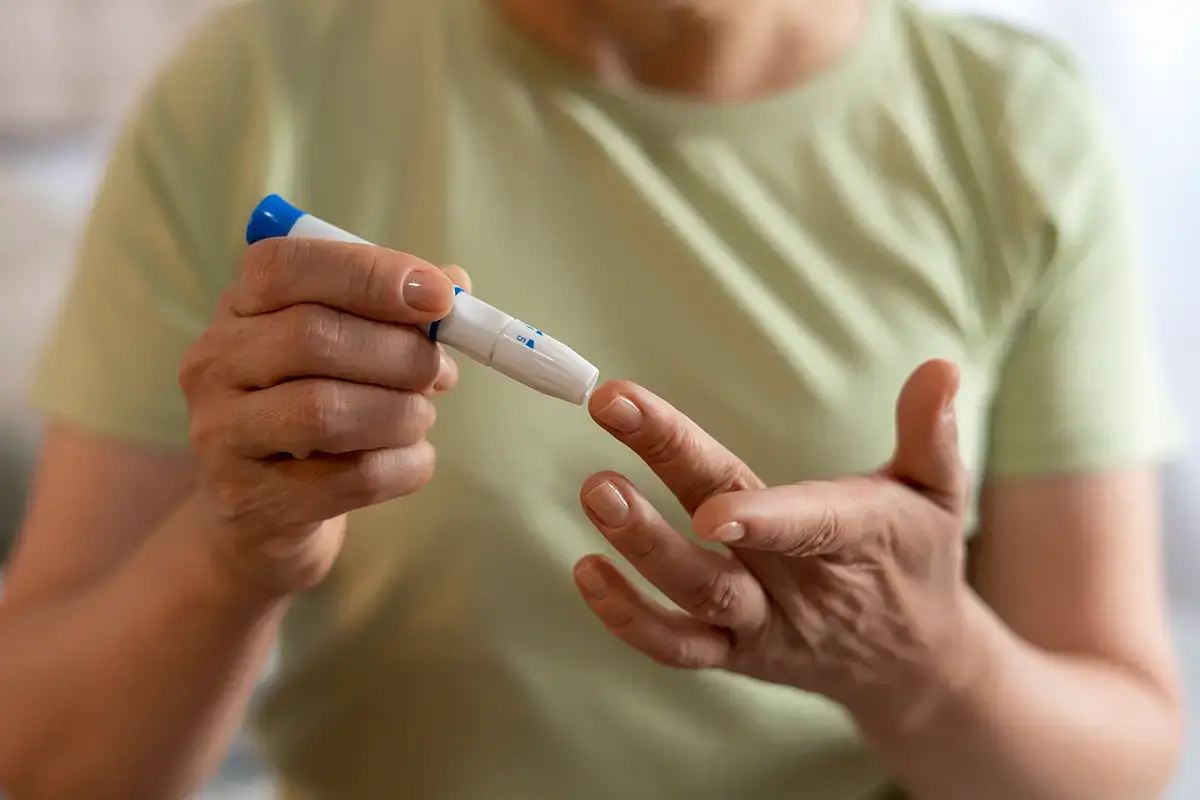
Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, excessive hunger, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision. Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that measure fasting blood glucose levels and, in some cases, the hemoglobin A1C test to assess long-term glycemic control.
Complications of Diabetes:
Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to a range of serious complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, neuropathy (nerve damage), retinopathy (eye damage), and foot problems that may lead to amputation. Effectively managing diabetes is essential to prevent or delay the development of these complications.
Treatments and Management:
Diabetes treatment aims to maintain blood glucose levels within the normal range to reduce the risk of complications. This often involves a combination of a balanced diet, regular physical activity, monitoring blood glucose levels, and in many cases, medication or insulin. New therapies and technologies, such as insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring, are helping improve diabetes management, offering patients more personalized and effective options.
Prevention of Diabetes:
Preventing type 2 diabetes primarily involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a healthy body weight, following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, limiting the intake of sugary and saturated fat-rich foods, and engaging in regular physical activity.
Social and Economic Impact:
In addition to the direct impact on individual health, diabetes also represents a significant burden on healthcare systems and global economies. The costs associated with treating diabetes and its complications are substantial, encompassing direct medical expenses as well as productivity losses and broader economic impact.
Education and Awareness:
Promoting education about diabetes and increasing awareness of risk factors, signs and symptoms, as well as prevention and management strategies, are critical to addressing the growing challenge of this global disease. Public health campaigns and community initiatives play a crucial role in disseminating accurate information and promoting healthy lifestyles.
Conclusion:
Diabetes is a serious condition that requires a holistic, multidisciplinary approach to effective management. Understanding the different types of diabetes, their symptoms, potential complications, and prevention strategies is essential to improving health outcomes and quality of life for millions worldwide.
Sources Consulted:
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Ministry of Health
- International epidemiological data on diabetes