How Caffeine Works in the Human Body and Its Benefits as a Pre-Workout
Caffeine is a widely consumed substance worldwide, known for its stimulating properties and energizing effects. But how exactly does it work in our bodies, and why is it a popular pre-workout choice? Let’s explore the mechanisms behind caffeine and its benefits for those looking to enhance physical performance.
How Caffeine Works in the Human Body
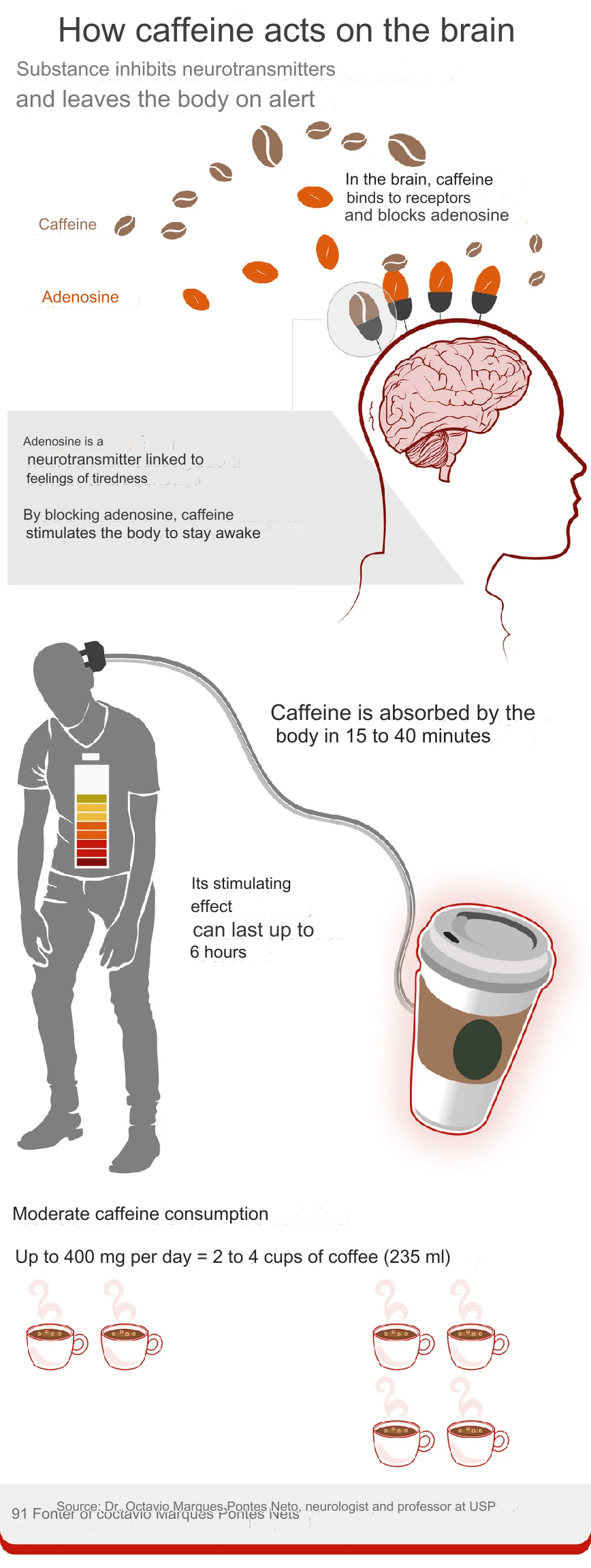
When we consume caffeine, it is quickly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and distributed throughout the body. The primary way caffeine exerts its effects is by blocking adenosine receptors in the brain. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that promotes sleep and relaxation. By blocking these receptors, caffeine prevents adenosine from exerting its calming effect, resulting in increased alertness and wakefulness .
Additionally, caffeine increases the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are associated with improved mood and alertness. These combined effects contribute to the feeling of energy and mental focus.
Benefits of Caffeine as a Pre-Workout
- Increased Energy: Caffeine is effective in boosting energy levels, making it a powerful ally before an intense workout session. It stimulates the central nervous system, helping to reduce the perception of effort during exercise.
- Improved Performance: Studies show that caffeine can enhance physical performance in endurance activities such as running and cycling, as well as in high-intensity, short-duration exercises like weightlifting .
- Fat Burning: Caffeine can also aid in fat burning by increasing thermogenesis and the mobilization of fatty acids from the body’s fat stores. This means it can help boost metabolic rate and calorie burn during exercise .
- Enhanced Concentration and Focus: Caffeine’s ability to improve concentration and mental focus is beneficial not only for physical performance but also for executing exercises with proper technique, reducing the risk of injury.
Final Considerations
While caffeine offers many benefits, it is important to consume this substance in moderation. High doses can lead to side effects such as insomnia, nervousness, and increased heart rate. It is recommended that healthy adults limit caffeine intake to about 400 mg per day, equivalent to approximately four cups of coffee .
Try incorporating caffeine into your pre-workout regimen and see how it can boost your performance. Always remember to listen to your body and adjust the dosage as needed.
Sources Consulted:
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. “Caffeine.” Accessed May 28, 2024.
- Mayo Clinic. “Caffeine: How much is too much?” Accessed May 28, 2024.
- WebMD. “Caffeine: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions.” Accessed May 28, 2024.
- Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. “Caffeine and performance.” Accessed May 28, 2024.
- Healthline. “Does Caffeine Increase Metabolism?” Accessed May 28, 2024.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “Spilling the Beans: How Much Caffeine is Too Much?” Accessed May 28, 2024.