Swimming Benefits: Health and Well-being in the Water
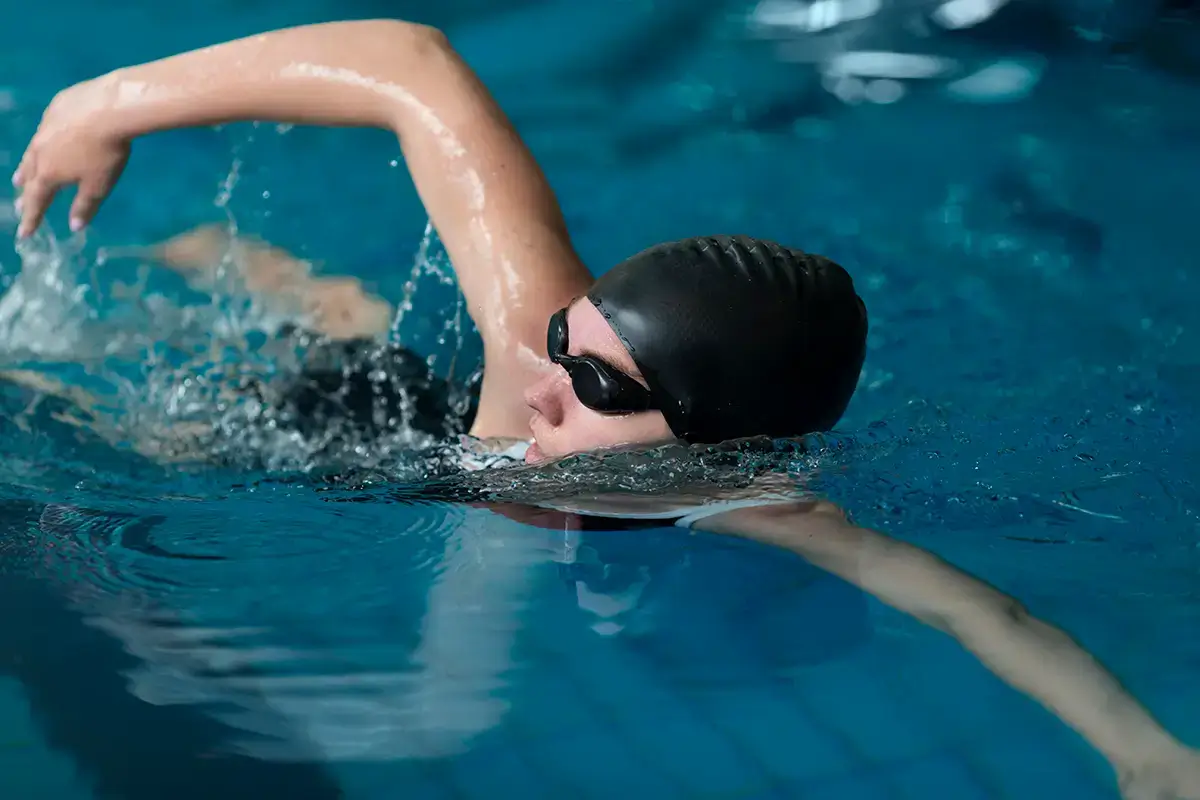
Swimming is much more than just a sport; it’s a complete physical activity that offers numerous benefits for both physical and mental health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), swimming is recommended as one of the best forms of exercise for people of all ages, due to its positive impact on cardiovascular fitness, muscular endurance, and flexibility (WHO, 2023). Moreover, it is a low-impact activity on joints, making it ideal for individuals with chronic medical conditions or those seeking a safe form of exercise.
Recent data from the Ministry of Health highlights that swimming is one of the most practiced physical activities in many countries, significantly contributing to public health improvement (Ministry of Health, 2023). With its therapeutic and recreational properties, swimming not only promotes physical health but also enhances emotional and psychological well-being of its practitioners.
Physical Benefits of Swimming:
Improved Cardiovascular Fitness: Swimming is an excellent aerobic exercise that strengthens the heart and enhances blood circulation. Regular practice can reduce the risk of heart disease and improve lung capacity.
Development of Muscle Strength and Endurance: Swimming engages all major muscle groups including back, arms, legs, abdominals, and core muscles. This helps in balanced muscle development and endurance.
Low Impact on Joints: Unlike many other sports, swimming is low impact, providing an excellent cardiovascular workout without putting excessive pressure on joints, thus suitable for all ages and physical conditions.
Increased Flexibility: The repetitive movements in water help improve overall body flexibility, reducing muscle stiffness and enhancing joint range of motion.
Mental and Emotional Benefits of Swimming:
Stress and Anxiety Reduction: Swimming is known for its calming and relaxing effect on the mind. The aquatic environment and fluid movements help alleviate stress and promote a sense of well-being.
Mood Enhancement: The release of endorphins during water exercise can elevate mood and combat mild to moderate depression.
Cognitive Stimulation: Breath control and concentration required during swimming can benefit cognitive functions such as memory and focus.
Practical Considerations and Safety:
Swimming Lessons and Proper Supervision: For beginners, participating in swimming lessons with qualified instructors is recommended to learn correct techniques and ensure safety in the water.
Safety Equipment: Using safety equipment such as life jackets, especially for children and beginners, is essential to prevent accidents.
Conclusion:
Swimming is not just a sport, but an activity that offers a wide range of benefits for physical, mental, and emotional health. By incorporating swimming into your weekly routine, you not only improve overall physical fitness but also promote a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Sources Cited:
- World Health Organization (WHO), 2023
- Ministry of Health, 2023