What is an Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injury?
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a crucial structure located in the knee that connects the femur to the tibia. Its primary function is to provide stability to the knee joint, especially during movements involving rotation or sudden changes in direction. ACL injuries are common in sports such as soccer, basketball, and skiing, where these types of movements frequently occur.
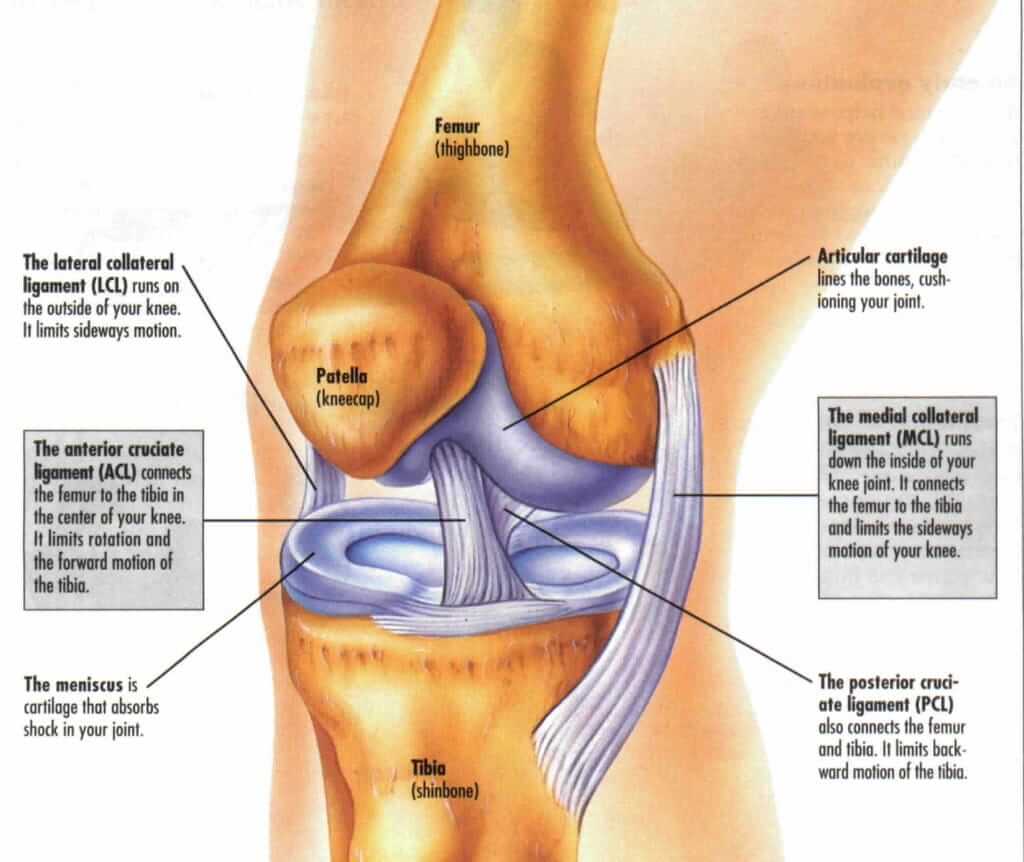
How does an ACL injury happen?
ACL tears typically occur due to:
- Abrupt movements: Such as sudden stops, changes in direction, or poorly executed landings after a jump.
- Direct impact: When the knee is subjected to significant lateral force, common during collisions in contact sports.
Signs and symptoms
The main signs of an ACL injury include:
- A popping sound at the time of injury;\n- Intense and immediate pain;\n- Swelling in the knee within a few hours;\n- Instability when trying to bear weight on the leg;\n- Difficulty or inability to perform certain movements.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing an ACL injury usually involves:
- Clinical examination: Evaluating the knee’s mobility and stability.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): To confirm the injury and check if other knee components are also affected.
- X-rays: Typically used to rule out associated fractures.
Primary treatment options
Treatment for ACL injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury, the patient’s age, and activity level. It is generally divided into two categories: conservative and surgical.
1. Conservative treatment
Ideal for less active patients or those with partial tears, conservative treatment includes:
- Physical therapy: Strengthening the muscles around the knee to improve stability.
- Use of braces: Support to limit excessive knee movements.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers for pain management.
2. Surgical treatment
Recommended for complete tears or for individuals who wish to return to high-impact activities. Surgery typically involves an ACL reconstruction, where a graft replaces the torn ligament. Post-surgery care includes:
- Intense physical therapy: To regain muscle strength and range of motion.
- Recovery time: It can take 6 to 12 months, depending on the patient.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of ACL injuries, some recommended practices include:
- Muscle strengthening: Focus on leg and core muscles.
- Proprioceptive training: Exercises to improve balance and coordination.
- Proper techniques: Learning to perform movements like landings and direction changes safely.
An ACL injury can be challenging, but with proper treatment and dedication to rehabilitation, most people can regain their functions and return to activities. If you suspect an ACL injury, consult a specialist for an accurate diagnosis and a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Photo by: Freepik